Upload Artifacts to GCS
You can use the Upload Artifacts to GCS step in your CI pipelines to upload artifacts to Google Cloud Storage (GCS). For more information on GCS, go to the Google Cloud documentation on Uploads and downloads.
You need:
- Access to a GCS instance.
- A CI pipeline with a Build stage.
- Steps in your pipeline that generate artifacts to upload, such as by running tests or building code. The steps you use depend on what artifacts you ultimately want to upload.
- A GCP connector.
You can also upload artifacts to S3, upload artifacts to JFrog, and upload artifacts to Sonatype Nexus.
Add an Upload Artifacts to GCS step
In your pipeline's Build stage, add an Upload Artifacts to GCS step and configure the settings accordingly.
Here is a YAML example of a minimum Upload Artifacts to GCS step.
- step:
type: GCSUpload
name: upload report
identifier: upload_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_GCP_CONNECTOR_ID
bucket: YOUR_GCS_BUCKET
sourcePath: path/to/source
target: path/to/upload/location
Upload Artifacts to GCS step settings
The Upload Artifacts to GCS step has the following settings. Depending on the stage's build infrastructure, some settings might be unavailable or optional. Settings specific to containers, such as Set Container Resources, are not applicable when using a VM or Harness Cloud build infrastructure.
Name
Enter a name summarizing the step's purpose. Harness automatically assigns an Id (Entity Identifier) based on the Name. You can change the Id.
GCP Connector
The Harness connector for the GCP account where you want to upload the artifact. For more information, go to Google Cloud Platform (GCP) connector settings reference. This step supports GCP connectors that use access key authentication. It does not support GCP connectors that inherit delegate credentials.
Bucket
The GCS destination bucket name.
Source Path
Path to the file or directory that you want to upload.
You can also use glob patterns in the Source Path to match multiple files or file types. For example:
sourcePath: dist/*.zip # Upload all ZIP files in the dist directory
ignore: "*.tmp" # Exclude temporary files
If you want to upload a compressed file, you must use a Run step to compress the artifact before uploading it.
Target
Provide a path, relative to the Bucket, where you want to store the artifact. Do not include the bucket name; you specified this in Bucket.
If you don't specify a Target, Harness uploads the artifact to the bucket's main directory.
Run as User
Specify the user ID to use to run all processes in the pod, if running in containers. For more information, go to Set the security context for a pod.
Set container resources
Set maximum resource limits for the resources used by the container at runtime:
- Limit Memory: The maximum memory that the container can use. You can express memory as a plain integer or as a fixed-point number using the suffixes
GorM. You can also use the power-of-two equivalentsGiandMi. The default is500Mi. - Limit CPU: The maximum number of cores that the container can use. CPU limits are measured in CPU units. Fractional requests are allowed; for example, you can specify one hundred millicpu as
0.1or100m. The default is400m. For more information, go to Resource units in Kubernetes.
Timeout
Set the timeout limit for the step. Once the timeout limit is reached, the step fails and pipeline execution continues. To set skip conditions or failure handling for steps, go to:
View artifacts on the Artifacts tab
You can use the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin to publish artifacts to the Artifacts tab. To do this, add a Plugin step after the Upload Artifacts to GCS step.
- Visual
- YAML
Configure the Plugin step settings as follows:
- Name: Enter a name.
- Container Registry: Select a Docker connector.
- Image: Enter
plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher. - Settings: Add the following two settings as key-value pairs.
file_urls: Provide a GCS URL that uses the Bucket, Target, and artifact name specified in the Upload Artifacts to GCS step, such ashttps://storage.googleapis.com/GCS_BUCKET_NAME/TARGET_PATH/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION. If you uploaded multiple artifacts, you can provide a list of URLs.artifact_file: Provide any.txtfile name, such asartifact.txtorurl.txt. This is a required setting that Harness uses to store the artifact URL and display it on the Artifacts tab. This value is not the name of your uploaded artifact, and it has no relationship to the artifact object itself.
Add a Plugin step that uses the artifact-metadata-publisher plugin.
- step:
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://storage.googleapis.com/GCS_BUCKET_NAME/TARGET_PATH/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION
artifact_file: artifact.txt
connectorRef: Use the built-in Docker connector (account.harness.Image) or specify your own Docker connector.image: Must beplugins/artifact-metadata-publisher.file_urls: Provide a GCS URL that uses thebucket,target, and artifact name specified in the Upload Artifacts to GCS step, such ashttps://storage.googleapis.com/GCS_BUCKET_NAME/TARGET_PATH/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION. If you uploaded multiple artifacts, you can provide a list of URLs.artifact_file: Provide any.txtfile name, such asartifact.txtorurl.txt. This is a required setting that Harness uses to store the artifact URL and display it on the Artifacts tab. This value is not the name of your uploaded artifact, and it has no relationship to the artifact object itself.
Build logs and artifact files
When you run the pipeline, you can observe the step logs on the build details page. If the Upload Artifacts step succeeds, you can find the artifact on GCS. If you used the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin, you can find the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
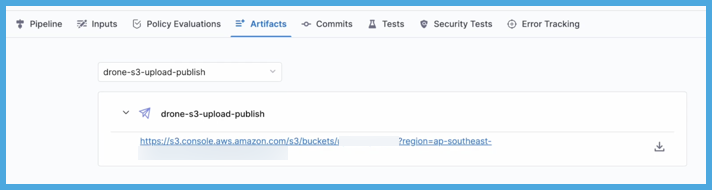
On the Artifacts tab, select the step name to expand the list of artifact links associated with that step.
If your pipeline has multiple steps that upload artifacts, use the dropdown menu on the Artifacts tab to switch between lists of artifacts uploaded by different steps.
Pipeline YAML examples
- Harness Cloud
- Self-managed
This example pipeline uses Harness Cloud build infrastructure. It produces test reports, uploads the reports to GCS, and uses the Artifact Metadata Publisher to publish the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
pipeline:
name: default
identifier: default
projectIdentifier: default
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
repoName: YOUR_CODE_REPO_NAME
build: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: test and upload artifact
identifier: test_and_upload_artifact
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
execution:
steps:
- step: ## Generate test reports.
type: Test
name: runTestsWithIntelligence
identifier: runTestsWithIntelligence
spec:
connectorRef: account.GCR
image: maven:3-openjdk-8
command: mvn test -Dmaven.test.failure.ignore=true -DfailIfNoTests=false
shell: Sh
intelligenceMode: true
reports:
- "target/surefire-reports/*.xml"
- step: ## Upload reports to GCS.
type: GCSUpload
name: upload report
identifier: upload_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_GCP_CONNECTOR_ID
bucket: YOUR_GCS_BUCKET
sourcePath: dist/*.zip # Supports glob patterns
target: <+pipeline.sequenceId>
- step: ## Show artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://storage.googleapis.com/YOUR_GCS_BUCKET/<+pipeline.sequenceId>/surefure-reports/
artifact_file: artifact.txt
This example pipeline uses a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure. It produces test reports, uploads the reports to GCS, and uses the Artifact Metadata Publisher to publish the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
pipeline:
name: allure-report-upload
identifier: allurereportupload
projectIdentifier: YOUR_HARNESS_PROJECT_ID
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
repoName: YOUR_CODE_REPO_NAME
build: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: build
identifier: build
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
infrastructure:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_KUBERNETES_CLUSTER_CONNECTOR_ID
namespace: YOUR_KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE
automountServiceAccountToken: true
nodeSelector: {}
os: Linux
execution:
steps:
- step: ## Generate test reports.
type: Test
name: runTestsWithIntelligence
identifier: runTestsWithIntelligence
spec:
connectorRef: account.GCR
image: maven:3-openjdk-8
command: mvn test -Dmaven.test.failure.ignore=true -DfailIfNoTests=false
shell: Sh
intelligenceMode: true
reports:
- "target/surefire-reports/*.xml"
- step: ## Upload reports to GCS.
type: GCSUpload
name: upload report
identifier: upload_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_GCP_CONNECTOR_ID
bucket: YOUR_GCS_BUCKET
sourcePath: dist/*.zip # Supports glob patterns
target: <+pipeline.sequenceId>
- step: ## Show artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://storage.googleapis.com/YOUR_GCS_BUCKET/<+pipeline.sequenceId>/surefire-reports/
artifact_file: artifact.txt
Download Artifacts from GCS
The Upload Artifacts to GCS step uses the GCS Drone plugin. While the plugin’s default behavior is to upload files from the local harness build node to a specified GCS bucket, we can reverse this behavior for download purposes when needed.
Modes of the GCS Drone Plugin
Default Operation (Upload Mode)
By default (i.e. when download is false), the Drone-gcs plugin uploads files. In this mode, it treats:
Source: The local file system on the harness build node.Target: The destination GCS bucket (extracted from theTargetconfiguration).
Download Mode
When the Download flag is set to true, the plugin reverses its behavior:
Source: Now points to the GCS bucket (extracted from theSourceconfiguration).Target: The local file system where files will be downloaded, as defined by theTargetconfiguration.
Download Options
You can download artifacts from GCS by:
Use the OOTB Step
The OOTB Upload Artifacts to GCS step in CI is designed to perform upload operations by default. However, since the Drone plugins/gcs plugin supports downloads when the PLUGIN_DOWNLOAD variable is set to true, you can simply pass this stage variable to switch the operation mode.
Configuration Steps
- Create a GCP Connector.
This works with an OIDC enabled connector as well. To learn more, go to Configure GCP with OIDC
- Add a pipeline stage variable named
PLUGIN_DOWNLOADand set ittrue. - Configure the pipeline. Add the Upload Artifacts to GCS step and select the GCP connector you created.
Example yaml:
- stage:
spec:
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: GCSUpload
name: GCSUpload_1
identifier: GCSUpload_1
spec:
connectorRef: gcp-oidc-connector
bucket: bucketName
sourcePath: YOUR_BUCKET_NAME/DIRECTORY
target: path/to/download/destination
variables:
- name: PLUGIN_DOWNLOAD
type: String
description: ""
required: false
value: "true"
Use a plugin step
The complete Plugin step settings can be configured as follows:
| Keys | Type | Description | Value example |
|---|---|---|---|
connectorRef | String | Select a Docker connector. | YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR |
image | String | Enter plugins/gcs. | plugins/gcs |
token | String | Reference to a Harness text secret containing a GCP service account token to connect and authenticate to GCS. | <+secrets.getValue("gcpserviceaccounttoken")> |
source | String | The directory or glob pattern to upload/download from your GCS bucket, specified as BUCKET_NAME/DIRECTORY or a glob. | my_cool_bucket/artifacts |
target | String | Path to the location where you want to store the downloaded artifacts, relative to the build workspace. | artifacts (downloads to /harness/artifacts) |
ignore | String | Glob pattern of files to exclude from the upload/download. | "*.tmp" |
download | Boolean | Must be true to enable downloading. If omitted or false, the plugin attempts to upload artifacts instead. | "true" |
The source and ignore fields support glob patterns. For example:
source: dist/*.zip # Upload all ZIP files in dist directory
target: my-bucket/builds
ignore: "*.tmp" # Exclude temporary files
For example:
- step:
type: Plugin
name: download
identifier: download
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_DOCKER_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/gcs
settings:
token: <+secrets.getValue("gcpserviceaccounttoken")>
source: YOUR_BUCKET_NAME/DIRECTORY
target: path/to/download/destination
download: "true"
Use a plugin step with OIDC
To enable OIDC authentication and perform download operations, you need to enable the following feature flags:
CI_SKIP_NON_EXPRESSION_EVALUATIONCI_ENABLE_OUTPUT_SECRETS
Contact Harness Support to enable these feature flags.
Then, create two plugin steps in your pipeline:
- Token Generation Step: This step uses the
plugins/gcp-oidcimage to generate an OIDC token and export it as output variable. - Download Operation Step: This step uses the
plugins/gcsimage to perform the download, consuming the token generated in the previous step.
Below is an example configuration:
Plugin Step 1: Generate the OIDC token
- step:
type: Plugin
name: generate-token
identifier: generate-token
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/gcp-oidc
settings:
project_id: 12345678
pool_id: 12345678
service_account_email_id: some-email@email.com
provider_id: service-account1
duration: 7200
Plugin Step 2: Execute the Download Operation
- step:
type: Plugin
name: download
identifier: download
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_DOCKER_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/gcs
settings:
token: <+steps.generate-token.output.outputVariables.GCLOUD_ACCESS_TOKEN>
source: YOUR_BUCKET_NAME/DIRECTORY
target: path/to/download/destination
download: "true"
Troubleshoot uploading artifacts
Go to the CI Knowledge Base for questions and issues related uploading artifacts, such as: