Publish anything to the Artifacts tab
You can use the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin to publish any URL on the Artifacts tab of the Build details page.
If you use AWS S3, you can use either the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin or the S3 Upload and Publish plugin, which combines the upload artifact and publish URL steps in one plugin.
Configure the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin
To use the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin, add a Plugin step to your CI pipeline.
For artifacts generated in the same pipeline, the Plugin step is usually placed after the step that uploads the artifact to cloud storage.
- step:
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://domain.com/path/to/artifact
Plugin step specifications
Use these specifications to configure the Plugin step to use the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin.
connectorRef
Use the built-in Docker connector (account.harness.Image) or specify your own Docker connector. Harness uses this to pull the plugin Docker image.
This setting is labeled Container Registry in the Visual editor.
image
Set to plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher.
file_urls
Provide the URL for the artifact you want to link on the Artifacts tab. In the Visual editor, set this as a key-value pair under Settings.
For artifacts in cloud storage, use the appropriate URL format for your cloud storage provider, for example:
- GCS:
https://storage.googleapis.com/GCS_BUCKET_NAME/TARGET_PATH/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION - S3:
https://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION
For artifacts uploaded through Upload Artifacts steps, use the Bucket, Target, and artifact name specified in the Upload Artifacts step.
For private S3 buckets, use the console view URL, such as https://s3.console.aws.amazon.com/s3/object/BUCKET?region=REGION&prefix=TARGET/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION.
If you uploaded multiple artifacts, you can provide a list of URLs, such as:
file_urls:
- https://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/artifact1.html
- https://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/artifact2.pdf
You can also set display name for each of the URLs set in the plugin, by using the format name:::file_url, where ::: is the delimiter that separates the name and url. For example:
file_urls:
- artifact1:::https://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/artifact1.html
- artifact2:::https://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/artifact2.pdf
For information about using Harness CI to upload artifacts, go to Build and push artifacts and images.
Artifact metadata publisher environment variables
The artifact-metadata-publisher plugin looks for two environment variables:
PLUGIN_ARTIFACT_FILE: The file path where the plugin stores artifact metadataPLUGIN_FILE_URLS: The URLs to be published to the Artifacts tab
The URLs passed via PLUGIN_FILE_URLS are stored in PLUGIN_ARTIFACT_FILE in the following JSON format, which the CI manager expects to publish under the Artifacts tab:
{
"kind": "fileUpload/v1",
"data": {
"fileArtifacts": [
{
"name": "file-0",
"url": "https://example.com/artifact"
}
]
}
}
Kubernetes flow differences
In Kubernetes flow, the CI manager doesn't automatically create the temporary file and pass it via PLUGIN_ARTIFACT_FILE (unlike cloud flow). You need to pass artifact_file: somefile.txt explicitly as input. The plugin then creates this file (somefile.txt) in the JSON format above, containing the URLs passed via PLUGIN_FILE_URLS input, which is then processed and displayed under the Artifacts tab in the pipeline.
- step:
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://domain.com/path/to/artifact
artifact_file: temp.txt
Using the plugin binary on hosted macOS runners
Hosted macOS runners cannot run Docker containers, which means you cannot use the containerized Plugin step with the artifact-metadata-publisher. Instead, you can download and run the plugin binary directly in a Run step.
Download and use the plugin binary
Use the following commands in a Run step to download the appropriate binary for macOS and publish artifacts:
- step:
type: Run
name: Publish Artifact Metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
shell: Sh
command: |-
# Download the artifact-metadata-publisher binary for macOS ARM64
curl -L https://github.com/drone-plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher/releases/download/v2.2.0/artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-arm64.zst -o artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-arm64.zst
# Decompress the binary
zstd -d artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-arm64.zst -o ./artifact-metadata-publisher
# Make the binary executable
chmod 700 ./artifact-metadata-publisher
# Run the plugin with your artifact URLs
PLUGIN_FILE_URLS="https://domain.com/path/to/artifact" ./artifact-metadata-publisher
Note
- Replace
v2.2.0with the latest version from the artifact-metadata-publisher releases. - For macOS Intel (x86_64), use
artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-amd64.zstinstead. - The CI manager automatically creates a temporary file and injects it via the
PLUGIN_ARTIFACT_FILEenvironment variable, so you don't need to create or manage this file manually.
Publish multiple artifacts with custom names
You can publish multiple artifacts and set custom display names using the format name:::url, where ::: is the delimiter between the name and URL:
- step:
type: Run
name: Publish Multiple Artifacts
identifier: publish_multiple_artifacts
spec:
shell: Sh
command: |-
curl -L https://github.com/drone-plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher/releases/download/v2.2.0/artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-arm64.zst -o artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-arm64.zst
zstd -d artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-arm64.zst -o ./artifact-metadata-publisher
chmod 700 ./artifact-metadata-publisher
# Publish multiple artifacts with custom names
PLUGIN_FILE_URLS="Config File:::https://s3.amazonaws.com/bucket/config.json,Build Report:::https://s3.amazonaws.com/bucket/report.html" ./artifact-metadata-publisher
Example: Publishing S3 presigned URLs
Here's a complete example that generates a presigned URL for an S3 artifact and publishes it to the Artifacts tab:
- step:
type: Run
name: Generate Presigned URL
identifier: generate_presigned_url
spec:
shell: Sh
command: |-
FILE_NAME="my-artifact.zip"
# Generate presigned URL (assumes AWS credentials are configured)
PRESIGNED_URL=$(aws s3 presign s3://my-bucket/$FILE_NAME --expires-in 3600)
echo "Generated presigned URL: $PRESIGNED_URL"
envVariables:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: <+secrets.getValue("aws_access_key")>
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: <+secrets.getValue("aws_secret_key")>
outputVariables:
- name: PRESIGNED_URL
- step:
type: Run
name: Publish Artifact Metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
shell: Sh
command: |-
curl -L https://github.com/drone-plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher/releases/download/v2.2.0/artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-arm64.zst -o artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-arm64.zst
zstd -d artifact-metadata-publisher-darwin-arm64.zst -o ./artifact-metadata-publisher
chmod 700 ./artifact-metadata-publisher
# Use the presigned URL from the previous step
PLUGIN_FILE_URLS="my-artifact.zip:::<+execution.steps.generate_presigned_url.output.outputVariables.PRESIGNED_URL>" ./artifact-metadata-publisher
Build logs and artifact files
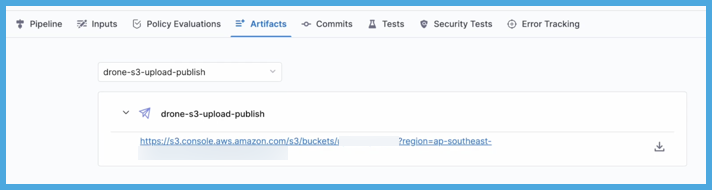
When you run the pipeline, you can observe the step logs on the Build details page, and you can find the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
On the Artifacts tab, select the step name to expand the list of artifact links associated with that step.
If your pipeline has multiple steps that upload artifacts, use the dropdown menu on the Artifacts tab to switch between lists of artifacts uploaded by different steps.
Tutorial: Upload an Allure report to the Artifacts tab
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the Artifacts Metadata Publisher plugin by generating and uploading an Allure report.
Part 1: Prepare cloud storage
-
You need access to a cloud storage provider. This tutorial uses GCS. If you use another option, you'll need to modify some of the steps according to your chosen cloud storage provider.
-
If you use S3, GCS, or JFrog, you need a Harness connector to use with the Upload Artifact step:
- S3: AWS connector
- GCS: GCP connector
- JFrog: Artifactory connector
tipStore authentication and access keys for connectors as Harness secrets.
-
In your cloud storage, create a bucket or repo where you can upload your artifact.
To access the artifact directly from the Artifacts tab, the upload location must be publicly available. If the location is not publicly available, you might need to log in to view the artifact or use a different artifact URL (such as a console view URL). This tutorial uses a publicly available GCS bucket to store the report.
Part 2: Prepare artifacts to upload
Add steps to your pipeline that generate and prepare artifacts to upload, such as Run steps. The steps you use depend on what artifacts you ultimately want to upload.
For example, this tutorial uses three Run steps to generate and prepare an artifact:
- The first step runs tests with Maven.
- The second step generates an Allure report. To ensure the build environment has the Allure tool, the step uses a Docker image that has this tool:
solutis/allure:2.9.0. - The third step combines the Allure report into a single HTML file.
- To view an Allure report in a browser, you must run a web server with the
allure opencommand; however, this command won't persist after the CI pipeline ends. Instead, use the allure-combine tool to convert the Allure report into a single HTML file. - Running the
allure-combine .command insideallure-reportgenerates thecomplete.htmlfile. - To ensure the build environment as access to the allure-combine tool, you can include steps to install it or use a Docker image that has the tool, such as
shubham149/allure-combine:latest.
- To view an Allure report in a browser, you must run a web server with the
- step:
type: Run
name: run maven tests
identifier: run_maven_tests
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: openjdk:11
shell: Sh
command: ./mvnw clean test site
- step:
type: Run
name: generate allure report
identifier: generate_allure_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: solutis/allure:2.9.0
command: |
cd target
allure generate allure-results --clean -o allure-report
- step:
type: Run
name: combine report
identifier: combine_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: shubham149/allure-combine:latest
command: |
cd target/allure-report
allure-combine .
cd ../..
cp target/allure-report/complete.html .
Part 3: Upload to cloud storage
Add a step to upload your artifact to cloud storage:
- Upload Artifacts to JFrog
- Upload Artifacts to GCS
- Upload Artifacts to S3
- Upload Artifacts to Sonatype Nexus
For example, this tutorial uploads the combined Allure report to GCS:
- step:
type: GCSUpload
name: upload report
identifier: upload_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_GCP_CONNECTOR_ID
bucket: YOUR_GCS_BUCKET
sourcePath: target/allure-report/complete.html
target: <+pipeline.sequenceId>
The target value uses a Harness expression, <+pipeline.sequenceId>, to ensure that artifacts uploaded by this pipeline are stored in unique directories and don't overwrite one another.
Part 4: Add URLs to the Artifacts tab
At this point, you can run the pipeline and then manually find the uploaded artifact in your cloud storage bucket or repo. Alternately, you can use the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin, which makes it easier to find the artifact directly associated with a particular build.
For example, this step publishes the URL for the combined Allure report on the Artifacts tab:
- step:
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://storage.googleapis.com/YOUR_GCS_BUCKET/<+pipeline.sequenceId>/complete.html
For details about these settings, go to Configure the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin.
Tutorial YAML examples
These YAML examples demonstrate the pipeline created in the preceding tutorial. This pipeline:
- Builds a Java Maven application.
- Generates and compiles an Allure report.
- Uploads the report to cloud storage.
- Provides a URL to access the report from the Artifacts tab in Harness.
- Harness Cloud
- Self-managed
This example uses Harness Cloud build infrastructure and uploads the Allure report artifact to GCS.
pipeline:
name: allure-report-upload
identifier: allurereportupload
projectIdentifier: YOUR_HARNESS_PROJECT_ID
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
repoName: YOUR_CODE_REPO_NAME
build: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: test and upload artifact
identifier: test_and_upload_artifact
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: run maven tests
identifier: run_maven_tests
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: openjdk:11
shell: Sh
command: ./mvnw clean test site
- step:
type: Run
name: generate allure report
identifier: generate_allure_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: solutis/allure:2.9.0
command: |
cd target
allure generate allure-results --clean -o allure-report
- step:
type: Run
name: combine report
identifier: combine_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: shubham149/allure-combine:latest
command: |
cd target/allure-report
allure-combine .
cd ../..
cp target/allure-report/complete.html .
- step:
type: GCSUpload
name: upload report
identifier: upload_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_GCP_CONNECTOR_ID
bucket: YOUR_GCS_BUCKET
sourcePath: target/allure-report/complete.html
target: <+pipeline.sequenceId>
- step:
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://storage.googleapis.com/YOUR_GCS_BUCKET/<+pipeline.sequenceId>/complete.html
This example uses a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure and uploads the Allure report artifact to GCS.
pipeline:
name: allure-report-upload
identifier: allurereportupload
projectIdentifier: YOUR_HARNESS_PROJECT_ID
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
repoName: YOUR_CODE_REPO_NAME
build: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: build
identifier: build
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
infrastructure:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_KUBERNETES_CLUSTER_CONNECTOR_ID
namespace: YOUR_KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE
automountServiceAccountToken: true
nodeSelector: {}
os: Linux
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: run maven tests
identifier: run_maven_tests
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: openjdk:11
shell: Sh
command: ./mvnw clean test site
- step:
type: Run
name: generate allure report
identifier: generate_allure_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: solutis/allure:2.9.0
command: |
cd target
allure generate allure-results --clean -o allure-report
- step:
type: Run
name: combine report
identifier: combine_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: shubham149/allure-combine:latest
command: |
cd target/allure-report
allure-combine .
cd ../..
cp target/allure-report/complete.html .
- step:
type: GCSUpload
name: upload report
identifier: upload_report
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_GCP_CONNECTOR_ID
bucket: YOUR_GCS_BUCKET
sourcePath: target/allure-report/complete.html
target: <+pipeline.sequenceId>
- step:
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://storage.googleapis.com/YOUR_GCS_BUCKET/<+pipeline.sequenceId>/complete.html
See also
- View test reports on the Artifacts tab
- View code coverage reports on the Artifacts tab
- View GCS artifacts on the Artifacts tab
- View JFrog artifacts on the Artifacts tab
- View Sonatype Nexus artifacts on the Artifacts tab
- View S3 artifacts on the Artifacts tab
Troubleshoot the Artifacts tab
Go to the CI Knowledge Base for questions and issues related to the Artifacts tab, such as: